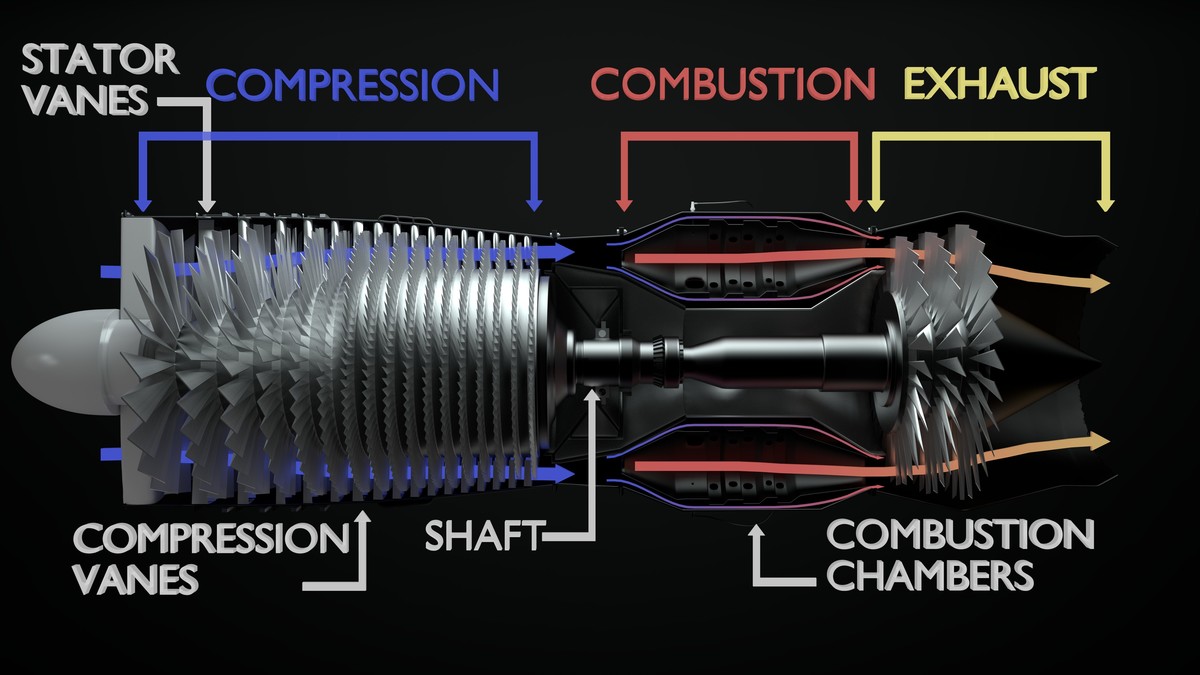
Jet Engine Cutaway with Diagram CG Cookie
An inside look at how jet engines work. Most modern jet propelled airplanes use a turbofan design, where incoming air is divided between a large fan and the.

What is the difference between a turbofan and a turboprop engine
Jet engines move the airplane forward with a great force that is produced by a tremendous thrust and causes the plane to fly very fast. All jet engines, which are also called gas turbines , work on the same principle. The engine sucks air in at the front with a fan. A compressor raises the pressure of the air.

jet engine Where does turbine vane and blade cooling air come from
Jet engines are complicated pieces of machinery with many moving parts. To help understand how the machines work, engineers often draw simplified diagrams, called schematics, of the engine. The schematic is often a flat, two-dimensional drawing of the engine representing the important components.
Definition > Jet engine
Discover the inner workings of a jet engine with a detailed schematic diagram, illustrating the various components and their functions. Learn how air is compressed, fuel is injected, and combustion occurs to produce thrust and power the aircraft. Explore the intricate design and engineering behind these powerful machines.
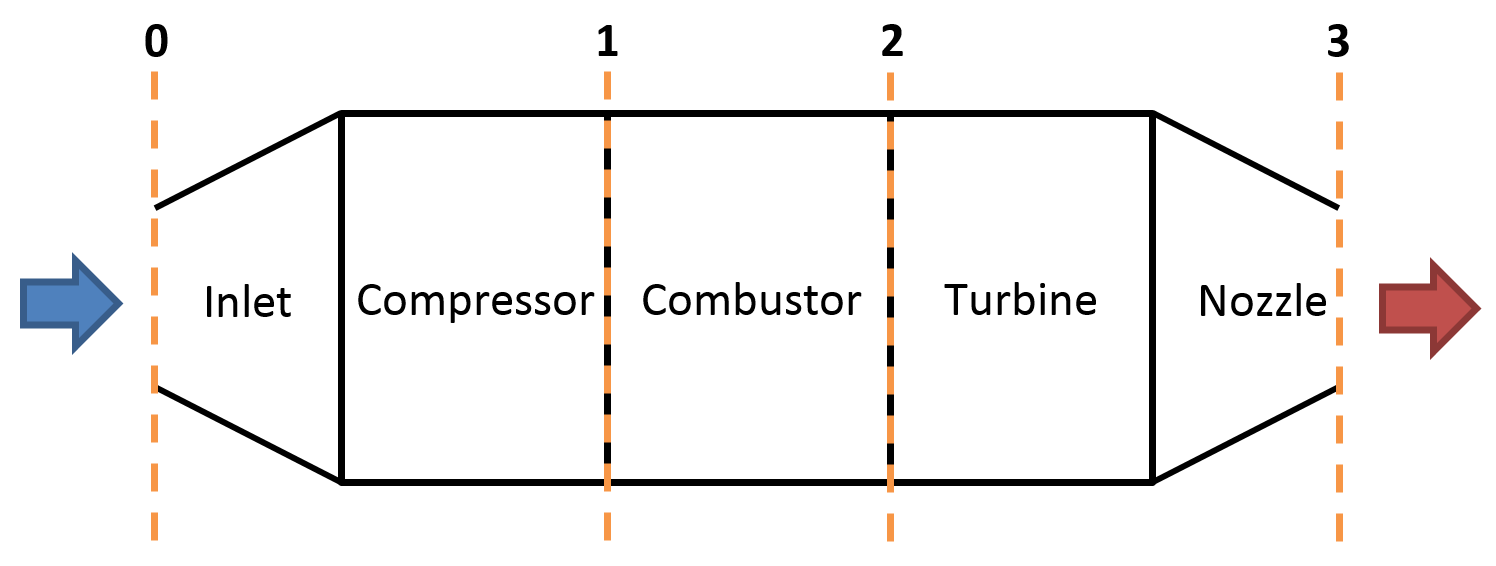
How does a jet engine work? Brayton thermodynamic cycle and
Glenn Research Center Most modern passenger and military aircraft are powered by gas turbine engines, which are also called jet engines. Jet engines come in a variety of shapes and sizes but all jet engines have certain parts in common.

Jet Engine
jet engine, any of a class of internal-combustion engines that propel aircraft by means of the rearward discharge of a jet of fluid, usually hot exhaust gases generated by burning fuel with air drawn in from the atmosphere. General characteristics The prime mover of virtually all jet engines is a gas turbine.

Airplane Engines (part 2) Jet Engines Back To First Principles
A jet engine is a machine that converts energy-rich, liquid fuel into a powerful pushing force called thrust. The thrust from one or more engines pushes a plane forward, forcing air past its scientifically shaped wings to create an upward force called lift that powers it into the sky. That, in short, is how planes work —but how do jet engines work?

aircraft design Could turbine or compressor stages of a jet engine be
A jet engine is a highly complex piece of equipment with a straightforward job: to give an airplane the thrust it needs to fly.. This diagram shows the path of the air that bypasses the core.

Main components of a jet engine Download Scientific Diagram
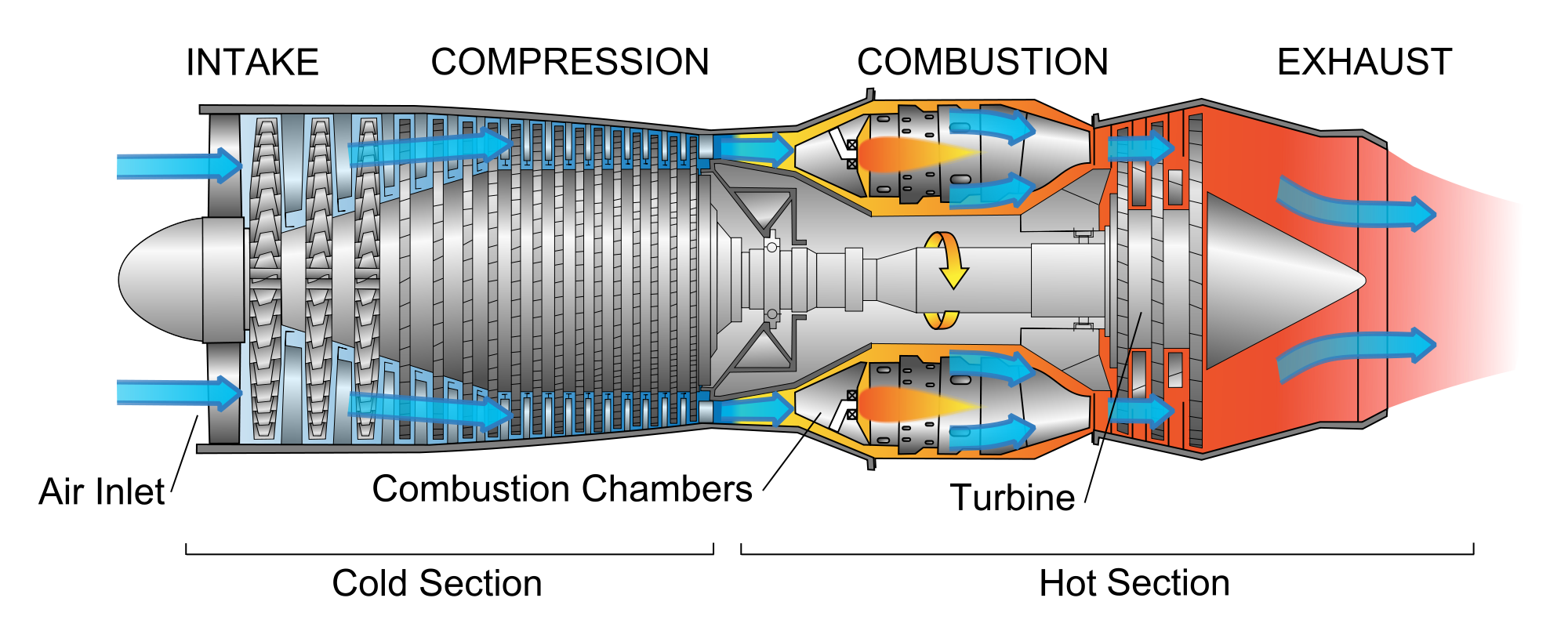
Diagram of a typical gas turbine jet engine. Air is compressed by the compressor blades as it enters the engine, and it is mixed and burned with fuel in the combustion section. The hot exhaust gases provide forward thrust and turn the turbines which drive the compressor blades. 1. Intake 2. Low pressure compression 3. High pressure compression 4.

How a jet engine works Business Insider
What is a Jet Engine? A jet engine is a machine designed for the purpose of creating large volumes of high-velocity exhaust gasses. (This sounds simplistic, but it is essentially correct.) This is done in order to produce the thrust needed to overcome the aerodynamic drag of an airplane.

(a) Schematic diagram of a jet engine; (b) a turbine blade; (c) a
Below is an animation of an isolated jet engine, which illustrates the process of air inflow, compression, combustion, air outflow and shaft rotation just described. The process can be described by the following diagram adopted from the website of Rolls Royce, a popular manufacturer of jet engines.

Details 78+ turbojet engine sketch in.eteachers
A gas turbine jet engine works by compressing air, mixing it with fuel, igniting the mixture, and ejecting the air behind the engine, creating a pushing force known as thrust. The engine does this using the basic principle of intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust, known as the Brayton cycle. This continuous cycle is what allows the.
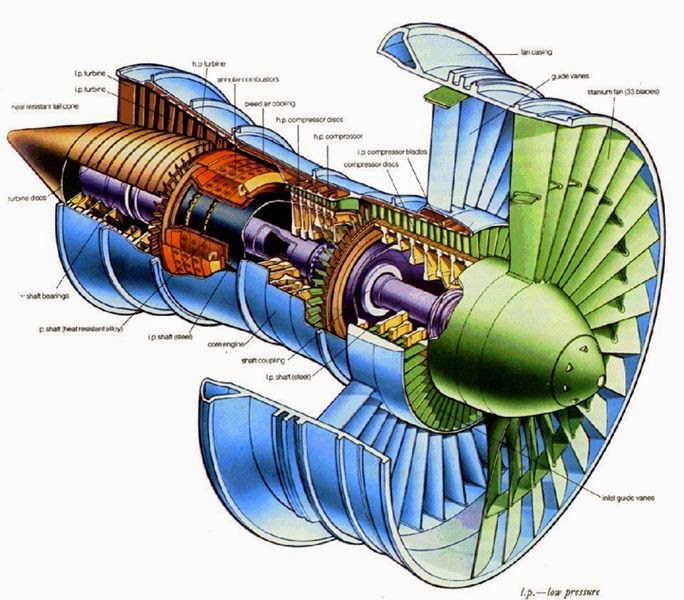
main components of jet engine Electrical Engineering Pics
A jet engine converts the liquid fuel into a strong force named as thrust. This force works for pushing the jet forward.
Let’s talk about jets, baby Jet engines, to be more precise Ars Technica
Definition, Parts, Diagram, Working, Applications Written by MechStudies in Articles, Automotive In this article, we will learn the basics of jet engines along with working, parts, diagrams, applications, etc. Also, we will explore how does a jet engine work. Let's explore the jet engine and it's working! What are Jet Engines? Definition

PW615 VLJ Jet Engine / 3D diagram by Charles Floyd at
Diagram of a typical gas turbine jet engine. Air is compressed by the fan blades as it enters the engine, and it is mixed and burned with fuel in the combustion section. The hot exhaust gases provide forward thrust and turn the turbines which drive the compressor fan blades. (Photo credit: Wikipedia) 1.1 The Turbojet

The science behind how jet engines works?
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine, discharging a fast-moving jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion.